
The first test you need to make for a router is to ping it, or send it a signal that proves not only that the router is there but also that your computer is connected to the router and that all communications are taking place in a friendly manner.
Allegiance Benefit Plan Management, Inc. Complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. Purchasing home insurance for your Texas property is a big step. Though it may seem easy enough to find a policy, getting the right coverage, at the right price, is critically important. At Allegiance Insurance Agency, we help homeowners to find the best possible combination of coverage and low cost. Allegiance insurance.
To send the router a friendly ping, follow these steps:
From the Start menu, choose All Programs→Accessories→Command Prompt.
A Command Prompt window opens.
To discover the router’s address, type ipconfig and press Enter.
The ipconfig command coughs up some information about your PC’s current network configuration. You see information that includes something like this:
The IPv4 address is your PC’s IP address on the local network. The address is assigned by the router, using something called DHCP.
The subnet mask is a type of filter that helps PCs on the network better see each other.
The default gateway is the IP address of the router. Make a note of it.
If you see the message, media disconnected, check both ends of the Ethernet cable.
Type the command ping, a space, and then the IP address of the router, or default gateway; press Enter.
For example, using the output shown in Step 2, the command is
After you press the Enter key, the ping command attempts to send four packets of information to the router, which should echo those results to you. You see something like this:
The information is technical, but not complex. The key is that you want to see a mess of data, as shown in the previous example. When you see the text Destination host unreachable or Request timed out, that’s when the PC has trouble communicating with the router.
Type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
Are there problems? You may not seem to see any, but first confirm that the gateway address given in Step 2 is the same as the router address. If not, the PC is most likely just pinging itself in Step 3. That works, but it’s not the same as communicating with the router.
When the router is unreachable, you probably need to turn off the router and then turn it on again. Because most routers lack a Power button, you need to unplug it and then plug it back in. After the power is back on, try repeating these steps to see whether you can ping the router.
If the router remains unreachable, you need to restart the entire network.
The ipconfig command’s output lists some Tunnel adapter information. Feel free to ignore it.
The router is also a gateway, which is why the results of the ipconfig command list its address as Default Gateway.
IP stands for Internet Protocol.
We all know how frustrating a slow internet connection can be. With CenturyLink’s free internet speed test, you can see how fast your upload and download speeds are, as well as more detailed statistics like jitter and ping to help you diagnose why your WiFi isn’t performing like it should. SpeedOf.Me is a broadband speed test that allows you to easily measure your actual Internet speed on all your devices like desktop, mobile, tablet, game console, smart TV, car, etc.
How Does Ping Work?Ping comes from a term used in sonar technology that sends out pulses of sound, and then listens for the echo to return. On a computer network, a ping tool is built into most operating systems that works in much the same way.
You issue the ping command along with a specific URL or IP address. Your computer sends several packets of information out to that device, and then waits for a response. When it gets the response, the ping tool shows you how long each packet took to make the round trip—or tells you there was no reply.It sounds simple, and it is. But you can use it to good effect. You can test whether your computer can reach another device—like your router—on your local network, or whether it can reach a device on the Internet. This can help you determine if a network problem is somewhere on your local network, or somewhere beyond. The time it takes packets to return to you can help you identify a slow connection, or if you’re experiencing packet loss.And it pretty much doesn’t matter what operating system you’re using.
Pull up a terminal or Command Prompt window, and you can use ping on macOS, Linux, or any version of Windows.RELATED: How to Use PingWe’re going to use the Windows Command Prompt in our example here. But you can also use the ping command in Windows PowerShell, or in the Terminal app on macOS or any Linux distro. Once you get to using the actual command, it works the same everywhere.In Windows, hit Windows+R. In the Run window, type “cmd” into the search box, and then hit Enter.At the prompt, type “ping” along with the URL or IP address you want to ping, and then hit Enter.
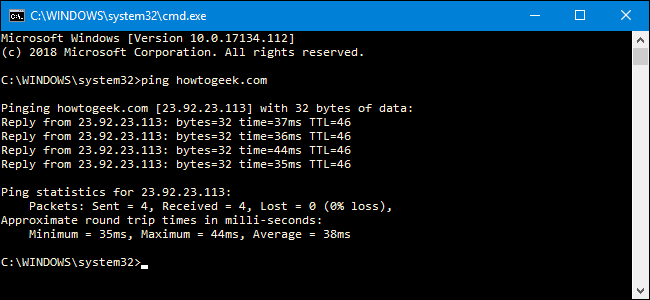
In the image below, we’re pinging www.howtogeek.com and getting a normal response.That response shows the URL you’re pinging, the IP address associated with that URL, and the size of the packets being sent on the first line. The next four lines show the replies from each individual packet, including the time (in milliseconds) it took for the response and the time-to-live (TTL) of the packet, which is the amount of time that must pass before the packet is discarded.At the bottom, you’ll see a summary that shows how many packets were sent and received, as well as the minimum, maximum, and average response time.And in the next image, we’re pinging the router on our local network using its IP address. We’re also getting a normal response from it.When the ping tool does not get a response from whatever devices you’re pinging, it lets you know that, too.And that’s how to use ping at its most basic. Of course, like most commands, there are some advanced switches you can use to make it behave a bit differently. For example, you can have it keep pinging a destination until you stop the command, specify the number of times you want it to ping, set how often it should ping, and more. But unless you’re doing some very specific types of troubleshooting, you won’t need to worry much about those advanced switches.If you’re curious about them, though, just type “ping /?” at the Command Prompt to see a list.So, What Can You Do With Ping?Now that you know how to use the command, here are some interesting things you can do with it:. Ping a URL (like www.howtogeek.com) or IP address to see if you can reach an internet destination.
If you get a successful response, you know that all the networking devices between you and that destination are working, including the network adapter in your computer, your router, and whatever devices exist on the internet between your router and the destination. And if you’re interested in exploring those routes further, you can use another to do just that. Ping a URL to resolve its IP address.
If you want know the IP address for a particular URL, you can ping the URL. The ping tool shows you right at the top the IP address it’s working with. Ping your router to see if you can reach it. If you can’t successfully ping an internet location, you can then try pinging your router.
A successful response lets you know that your local network is working okay, and that the problem reaching the internet location is somewhere out of your control. Ping your loopback address (127.0.0.1). If you can’t successfully ping your router, but your router appears to be turned on and working, you can try pinging what’s known as a loopback address. That address is always 127.0.0.1, and pinging it successfully lets you know that the network adapter on your computer (and the networking software in your OS) is working properly.Note: You may not get a ping response from other computers on your local network because the built-in firewalls on those devices prevent them from responding to ping requests. If you want to be able to ping those devices, you’ll need to turn off that setting to.The list above uses a kind of outside-in approach, where you ping the furthest destination first, and then work your way in to the more local devices. Some people like to work inside-out by pinging the loopback address first, then their router (or another local device), and then an internet address.And of course, what we’re talking about in this article is mostly about using ping to perform troubleshooting on a home or small business network. On larger networks, there’s a lot more complexity to worry about.
Plus, if you’re tasked with troubleshooting larger networks, you probably already know how to use ping and many other networking tools.
Popular Posts


The first test you need to make for a router is to ping it, or send it a signal that proves not only that the router is there but also that your computer is connected to the router and that all communications are taking place in a friendly manner.
Allegiance Benefit Plan Management, Inc. Complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. Purchasing home insurance for your Texas property is a big step. Though it may seem easy enough to find a policy, getting the right coverage, at the right price, is critically important. At Allegiance Insurance Agency, we help homeowners to find the best possible combination of coverage and low cost. Allegiance insurance.
To send the router a friendly ping, follow these steps:
From the Start menu, choose All Programs→Accessories→Command Prompt.
A Command Prompt window opens.
To discover the router’s address, type ipconfig and press Enter.
The ipconfig command coughs up some information about your PC’s current network configuration. You see information that includes something like this:
The IPv4 address is your PC’s IP address on the local network. The address is assigned by the router, using something called DHCP.
The subnet mask is a type of filter that helps PCs on the network better see each other.
The default gateway is the IP address of the router. Make a note of it.
If you see the message, media disconnected, check both ends of the Ethernet cable.
Type the command ping, a space, and then the IP address of the router, or default gateway; press Enter.
For example, using the output shown in Step 2, the command is
After you press the Enter key, the ping command attempts to send four packets of information to the router, which should echo those results to you. You see something like this:
The information is technical, but not complex. The key is that you want to see a mess of data, as shown in the previous example. When you see the text Destination host unreachable or Request timed out, that’s when the PC has trouble communicating with the router.
Type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
Are there problems? You may not seem to see any, but first confirm that the gateway address given in Step 2 is the same as the router address. If not, the PC is most likely just pinging itself in Step 3. That works, but it’s not the same as communicating with the router.
When the router is unreachable, you probably need to turn off the router and then turn it on again. Because most routers lack a Power button, you need to unplug it and then plug it back in. After the power is back on, try repeating these steps to see whether you can ping the router.
If the router remains unreachable, you need to restart the entire network.
The ipconfig command’s output lists some Tunnel adapter information. Feel free to ignore it.
The router is also a gateway, which is why the results of the ipconfig command list its address as Default Gateway.
IP stands for Internet Protocol.
We all know how frustrating a slow internet connection can be. With CenturyLink’s free internet speed test, you can see how fast your upload and download speeds are, as well as more detailed statistics like jitter and ping to help you diagnose why your WiFi isn’t performing like it should. SpeedOf.Me is a broadband speed test that allows you to easily measure your actual Internet speed on all your devices like desktop, mobile, tablet, game console, smart TV, car, etc.
How Does Ping Work?Ping comes from a term used in sonar technology that sends out pulses of sound, and then listens for the echo to return. On a computer network, a ping tool is built into most operating systems that works in much the same way.
You issue the ping command along with a specific URL or IP address. Your computer sends several packets of information out to that device, and then waits for a response. When it gets the response, the ping tool shows you how long each packet took to make the round trip—or tells you there was no reply.It sounds simple, and it is. But you can use it to good effect. You can test whether your computer can reach another device—like your router—on your local network, or whether it can reach a device on the Internet. This can help you determine if a network problem is somewhere on your local network, or somewhere beyond. The time it takes packets to return to you can help you identify a slow connection, or if you’re experiencing packet loss.And it pretty much doesn’t matter what operating system you’re using.
Pull up a terminal or Command Prompt window, and you can use ping on macOS, Linux, or any version of Windows.RELATED: How to Use PingWe’re going to use the Windows Command Prompt in our example here. But you can also use the ping command in Windows PowerShell, or in the Terminal app on macOS or any Linux distro. Once you get to using the actual command, it works the same everywhere.In Windows, hit Windows+R. In the Run window, type “cmd” into the search box, and then hit Enter.At the prompt, type “ping” along with the URL or IP address you want to ping, and then hit Enter.
In the image below, we’re pinging www.howtogeek.com and getting a normal response.That response shows the URL you’re pinging, the IP address associated with that URL, and the size of the packets being sent on the first line. The next four lines show the replies from each individual packet, including the time (in milliseconds) it took for the response and the time-to-live (TTL) of the packet, which is the amount of time that must pass before the packet is discarded.At the bottom, you’ll see a summary that shows how many packets were sent and received, as well as the minimum, maximum, and average response time.And in the next image, we’re pinging the router on our local network using its IP address. We’re also getting a normal response from it.When the ping tool does not get a response from whatever devices you’re pinging, it lets you know that, too.And that’s how to use ping at its most basic. Of course, like most commands, there are some advanced switches you can use to make it behave a bit differently. For example, you can have it keep pinging a destination until you stop the command, specify the number of times you want it to ping, set how often it should ping, and more. But unless you’re doing some very specific types of troubleshooting, you won’t need to worry much about those advanced switches.If you’re curious about them, though, just type “ping /?” at the Command Prompt to see a list.So, What Can You Do With Ping?Now that you know how to use the command, here are some interesting things you can do with it:. Ping a URL (like www.howtogeek.com) or IP address to see if you can reach an internet destination.
If you get a successful response, you know that all the networking devices between you and that destination are working, including the network adapter in your computer, your router, and whatever devices exist on the internet between your router and the destination. And if you’re interested in exploring those routes further, you can use another to do just that. Ping a URL to resolve its IP address.
If you want know the IP address for a particular URL, you can ping the URL. The ping tool shows you right at the top the IP address it’s working with. Ping your router to see if you can reach it. If you can’t successfully ping an internet location, you can then try pinging your router.
A successful response lets you know that your local network is working okay, and that the problem reaching the internet location is somewhere out of your control. Ping your loopback address (127.0.0.1). If you can’t successfully ping your router, but your router appears to be turned on and working, you can try pinging what’s known as a loopback address. That address is always 127.0.0.1, and pinging it successfully lets you know that the network adapter on your computer (and the networking software in your OS) is working properly.Note: You may not get a ping response from other computers on your local network because the built-in firewalls on those devices prevent them from responding to ping requests. If you want to be able to ping those devices, you’ll need to turn off that setting to.The list above uses a kind of outside-in approach, where you ping the furthest destination first, and then work your way in to the more local devices. Some people like to work inside-out by pinging the loopback address first, then their router (or another local device), and then an internet address.And of course, what we’re talking about in this article is mostly about using ping to perform troubleshooting on a home or small business network. On larger networks, there’s a lot more complexity to worry about.
Plus, if you’re tasked with troubleshooting larger networks, you probably already know how to use ping and many other networking tools.
...'>Ping Test(29.02.2020)

The first test you need to make for a router is to ping it, or send it a signal that proves not only that the router is there but also that your computer is connected to the router and that all communications are taking place in a friendly manner.
Allegiance Benefit Plan Management, Inc. Complies with applicable Federal civil rights laws and does not discriminate on the basis of race, color, national origin, age, disability, or sex. Purchasing home insurance for your Texas property is a big step. Though it may seem easy enough to find a policy, getting the right coverage, at the right price, is critically important. At Allegiance Insurance Agency, we help homeowners to find the best possible combination of coverage and low cost. Allegiance insurance.
To send the router a friendly ping, follow these steps:
From the Start menu, choose All Programs→Accessories→Command Prompt.
A Command Prompt window opens.
To discover the router’s address, type ipconfig and press Enter.
The ipconfig command coughs up some information about your PC’s current network configuration. You see information that includes something like this:
The IPv4 address is your PC’s IP address on the local network. The address is assigned by the router, using something called DHCP.
The subnet mask is a type of filter that helps PCs on the network better see each other.
The default gateway is the IP address of the router. Make a note of it.
If you see the message, media disconnected, check both ends of the Ethernet cable.
Type the command ping, a space, and then the IP address of the router, or default gateway; press Enter.
For example, using the output shown in Step 2, the command is
After you press the Enter key, the ping command attempts to send four packets of information to the router, which should echo those results to you. You see something like this:
The information is technical, but not complex. The key is that you want to see a mess of data, as shown in the previous example. When you see the text Destination host unreachable or Request timed out, that’s when the PC has trouble communicating with the router.
Type exit and press Enter to close the Command Prompt window.
Are there problems? You may not seem to see any, but first confirm that the gateway address given in Step 2 is the same as the router address. If not, the PC is most likely just pinging itself in Step 3. That works, but it’s not the same as communicating with the router.
When the router is unreachable, you probably need to turn off the router and then turn it on again. Because most routers lack a Power button, you need to unplug it and then plug it back in. After the power is back on, try repeating these steps to see whether you can ping the router.
If the router remains unreachable, you need to restart the entire network.
The ipconfig command’s output lists some Tunnel adapter information. Feel free to ignore it.
The router is also a gateway, which is why the results of the ipconfig command list its address as Default Gateway.
IP stands for Internet Protocol.
We all know how frustrating a slow internet connection can be. With CenturyLink’s free internet speed test, you can see how fast your upload and download speeds are, as well as more detailed statistics like jitter and ping to help you diagnose why your WiFi isn’t performing like it should. SpeedOf.Me is a broadband speed test that allows you to easily measure your actual Internet speed on all your devices like desktop, mobile, tablet, game console, smart TV, car, etc.
How Does Ping Work?Ping comes from a term used in sonar technology that sends out pulses of sound, and then listens for the echo to return. On a computer network, a ping tool is built into most operating systems that works in much the same way.
You issue the ping command along with a specific URL or IP address. Your computer sends several packets of information out to that device, and then waits for a response. When it gets the response, the ping tool shows you how long each packet took to make the round trip—or tells you there was no reply.It sounds simple, and it is. But you can use it to good effect. You can test whether your computer can reach another device—like your router—on your local network, or whether it can reach a device on the Internet. This can help you determine if a network problem is somewhere on your local network, or somewhere beyond. The time it takes packets to return to you can help you identify a slow connection, or if you’re experiencing packet loss.And it pretty much doesn’t matter what operating system you’re using.
Pull up a terminal or Command Prompt window, and you can use ping on macOS, Linux, or any version of Windows.RELATED: How to Use PingWe’re going to use the Windows Command Prompt in our example here. But you can also use the ping command in Windows PowerShell, or in the Terminal app on macOS or any Linux distro. Once you get to using the actual command, it works the same everywhere.In Windows, hit Windows+R. In the Run window, type “cmd” into the search box, and then hit Enter.At the prompt, type “ping” along with the URL or IP address you want to ping, and then hit Enter.
In the image below, we’re pinging www.howtogeek.com and getting a normal response.That response shows the URL you’re pinging, the IP address associated with that URL, and the size of the packets being sent on the first line. The next four lines show the replies from each individual packet, including the time (in milliseconds) it took for the response and the time-to-live (TTL) of the packet, which is the amount of time that must pass before the packet is discarded.At the bottom, you’ll see a summary that shows how many packets were sent and received, as well as the minimum, maximum, and average response time.And in the next image, we’re pinging the router on our local network using its IP address. We’re also getting a normal response from it.When the ping tool does not get a response from whatever devices you’re pinging, it lets you know that, too.And that’s how to use ping at its most basic. Of course, like most commands, there are some advanced switches you can use to make it behave a bit differently. For example, you can have it keep pinging a destination until you stop the command, specify the number of times you want it to ping, set how often it should ping, and more. But unless you’re doing some very specific types of troubleshooting, you won’t need to worry much about those advanced switches.If you’re curious about them, though, just type “ping /?” at the Command Prompt to see a list.So, What Can You Do With Ping?Now that you know how to use the command, here are some interesting things you can do with it:. Ping a URL (like www.howtogeek.com) or IP address to see if you can reach an internet destination.
If you get a successful response, you know that all the networking devices between you and that destination are working, including the network adapter in your computer, your router, and whatever devices exist on the internet between your router and the destination. And if you’re interested in exploring those routes further, you can use another to do just that. Ping a URL to resolve its IP address.
If you want know the IP address for a particular URL, you can ping the URL. The ping tool shows you right at the top the IP address it’s working with. Ping your router to see if you can reach it. If you can’t successfully ping an internet location, you can then try pinging your router.
A successful response lets you know that your local network is working okay, and that the problem reaching the internet location is somewhere out of your control. Ping your loopback address (127.0.0.1). If you can’t successfully ping your router, but your router appears to be turned on and working, you can try pinging what’s known as a loopback address. That address is always 127.0.0.1, and pinging it successfully lets you know that the network adapter on your computer (and the networking software in your OS) is working properly.Note: You may not get a ping response from other computers on your local network because the built-in firewalls on those devices prevent them from responding to ping requests. If you want to be able to ping those devices, you’ll need to turn off that setting to.The list above uses a kind of outside-in approach, where you ping the furthest destination first, and then work your way in to the more local devices. Some people like to work inside-out by pinging the loopback address first, then their router (or another local device), and then an internet address.And of course, what we’re talking about in this article is mostly about using ping to perform troubleshooting on a home or small business network. On larger networks, there’s a lot more complexity to worry about.
Plus, if you’re tasked with troubleshooting larger networks, you probably already know how to use ping and many other networking tools.
...'>Ping Test(29.02.2020)